Temperature Sensor Code
Create a new sketch in the Arduino IDE, and replace all the code in the sketch with the code from below.
Incomplete Code
This code is incomplete. You will need to make changes to it so that it works correctly. The changes you need to make are marked with comments starting with TODO, and are described in more detail below.
const int TEMPERATURE_ANALOG_PIN = 0;
// TODO Set these constants correctly using the temperature sensor datasheet
const float ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS = 0;
const float MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS = 1;
const int DELAY_MILLISECONDS = 1000;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// TODO use analogRead(pin) to read the voltage on TEMPERATURE_ANALOG_PIN
int adcValue = 0;
float millivolts = (((float) adcValue * 5) / 1024) * 1000;
float temperature = (millivolts - ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS) / MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS;
int roundedTemperature = round(temperature);
Serial.println(roundedTemperature);
delay(DELAY_MILLISECONDS);
}
There are a few different sections in the code above, and there a few things you need to change to get it to work correctly. All these items are described in the following sections.
Constants
All the code before the setup() function defines several constants. Constants are just like variables, except you can't change them. That's what makes them constants.
The first constant, TEMPERATURE_ANALOG_PIN, is set to 0 since you previously connected the temperature sensor's output to the A0 analog input on the Arduino.
The next two constants, ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS and MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS should be set to the number of millivolts (mV) the temperature sensor outputs when the temperature is 0 °C and the change in the sensor's output voltage, in millivolts, for each change of 1 °C in the measured temperature. The following table provides some examples of how the sensor's output voltage corresponds to temperature.
| Temperature (°C) | Sensor Output Voltage (mV) |
|---|---|
| 0 | ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS |
| 1 | ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS + (1 * MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS) |
| -1 | ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS + (-1 * MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS) |
| 2 | ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS + (2 * MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS) |
| -2 | ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS + (-2 * MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS) |
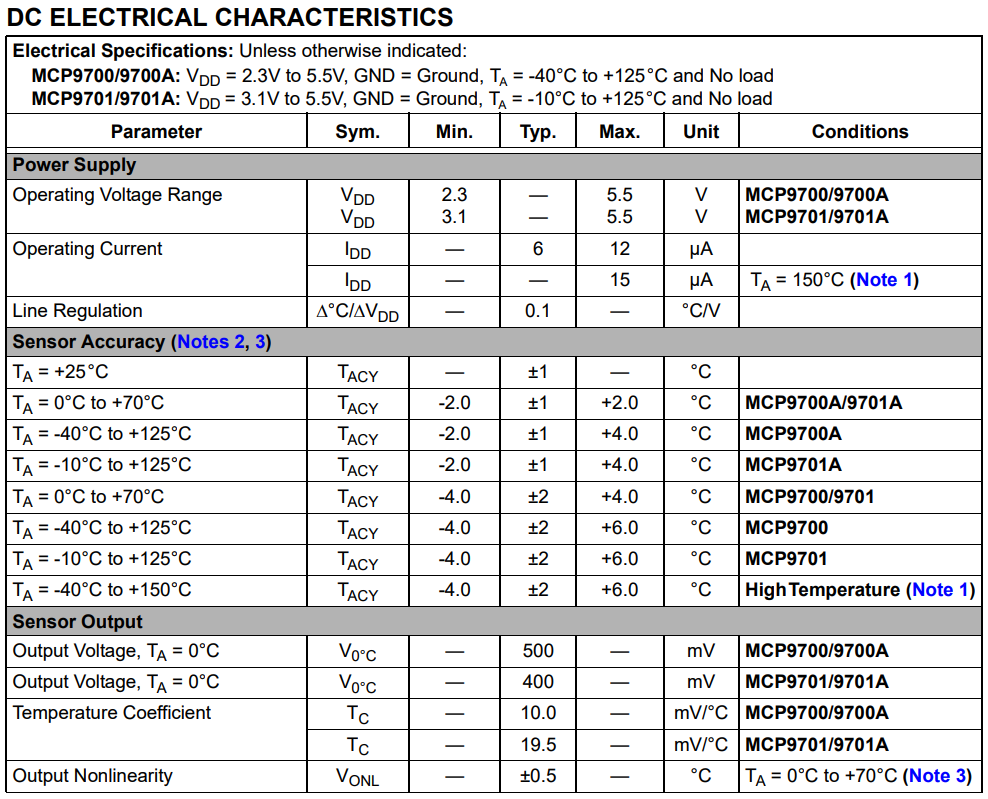
These constants are not currently set correctly. Using the portion of the temperature sensor datasheet below, set ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS and MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS to the correct values. If you get stuck try looking at the hints or answer below.
Temperature Sensor Part Number
This temperature sensor you are using is the MCP9701A. The datasheet contains values for several different models. Be sure to pick the right ones.
Hint #1
Look at the last portion of the table, titled "Sensor Output"
Hint #2
ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS should be set to the value for "Output Voltage, TA = 0°C"
Hint #3
MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS should be set to the value for "Temperature Coefficient"
Answer
const float ZERO_DEGREE_CELSIUS_MILLIVOLTS = 400;
const float MILLIVOLTS_PER_DEGREE_CELSIUS = 19.5;
The last constant, DELAY_MILLISECONDS, is the delay in milliseconds between temperature measurements.
Setup
The code in the setup() function initializes the serial port so that the Arduino can display the measured temperature on the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
Loop
The first thing the loop function does is read the voltage from the temperature sensor, however this line is not complete. To read the analog input pins, use the analogRead(pin) function. pin is the pin which will be read. Update the code to set adcValue to the value measured from the analog input where the temperature sensor output is connected. If you get stuck try looking at the hints or answer below.
Hint #1
The analog input pin the temperature sensor is connected to is already assigned to the constant TEMPERATURE_ANALOG_PIN.
Hint #2
int value = analogRead(3); would read the analog input A3 and store the reading in an integer variable named value. The 3 can be replaced with the name of a variable or constant that is set to the pin to read.
Answer
int adcValue = analogRead(TEMPERATURE_ANALOG_PIN);
After reading the analog pin, the temperature is calculated. First the adcValue is converted into millivolts, and then the temperature is calculated using the constants already defined. The variables millivolts and temperature have the type float and not the type int. This is because float can be used to represent numbers with decimal places, while int cannot. Since the display you are going to build will not have any decimal places, the temperature is rounded and stored in an int variable named roundedTemperature. The roundedTemperature value is then sent over the serial port to the computer.
At the end of the loop() function, the delay() function is used so that the program waits before measuring the temperature again.